Areas are one of four main data types in the Spatial Portal, along with species (taxa), layers and facets. Area can be defined by 14 different options. When an area gets defined, it is added to the map; a new layer is added to the layers list. Areas form the basis of most Spatial Portal operations either explicitly (by explicit definition) or implicitly (by defaulting to current map extents).

Areas are a persistent option associated with the display or analysis of species (taxa). NOTE: In dealing with complex areas that are either pre-existing in the Spatial Portal, created interactively or imported, or generated from an area merge, the area boundaries may be generalised. The reason for this is that the system has limitations on the number of vertices that can be readily processed through ALA functions. If the area is above the threshold, you will be given a warning that the area will be generalized to fit the limits.
As noted above, the analysis tools require a defined area – and all provide the facility to add a new area during a process – this help text also relates to the area selection process used within the analysis tools. There are thirteen ways to add an area to the map (grouped into five main categories):

Interact with the map
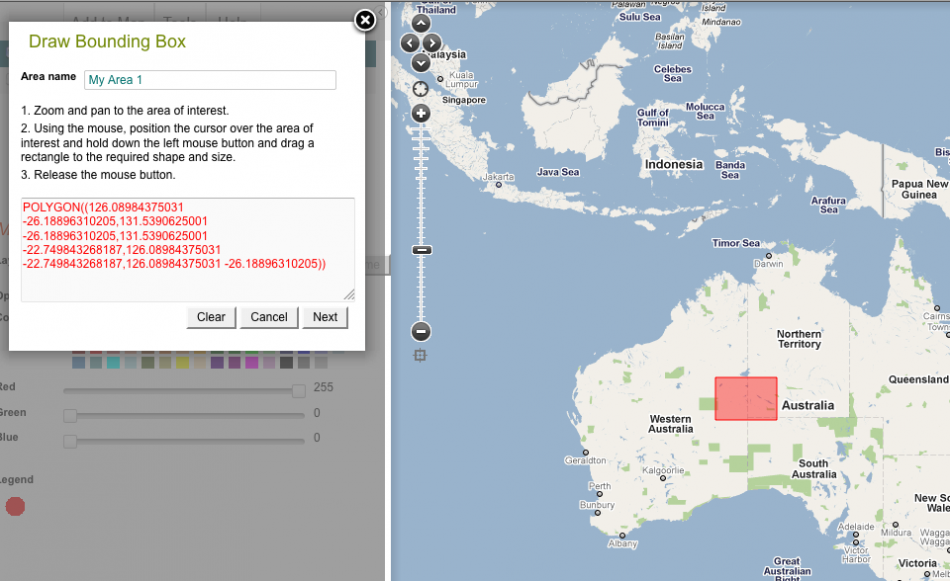
Interact with the map – allows the user to draw a region directly within the Spatial Portal. Sub-options available include drawing a bounding box, a polygon, a point and radius, or to select a pre-defined polygon area from a contextual layer that has already been mapped. Note that you should either zoom and pan to the area of interest before digitizing, or after the pop-up box appears – use the Google slider and direction functions to the left of the map as dragging operations will not work when the portal is looking for mouse operations on the map.
1. Draw bounding box
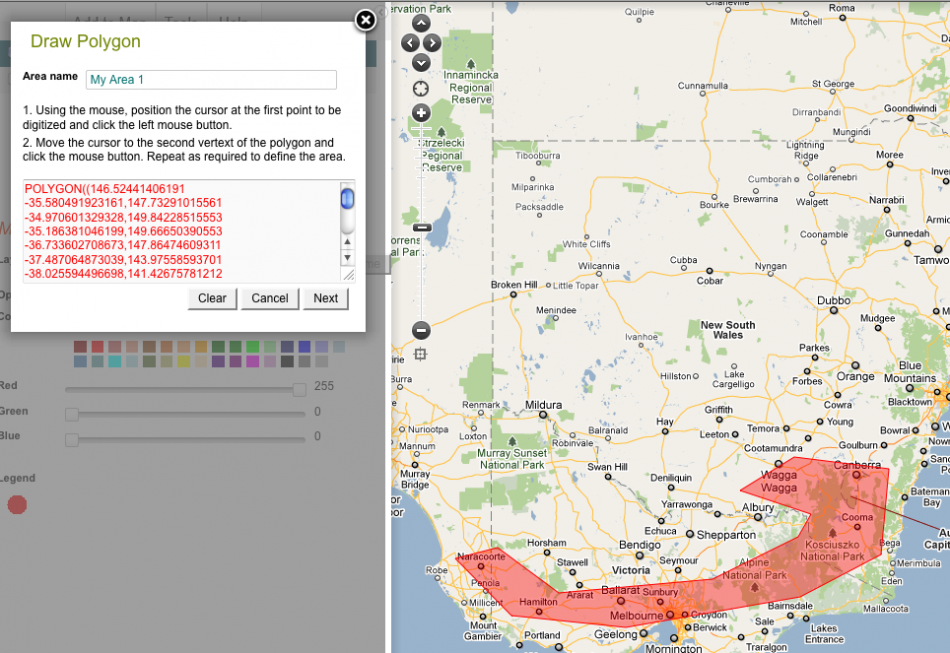
2. Draw polygon
3. Draw point and radius
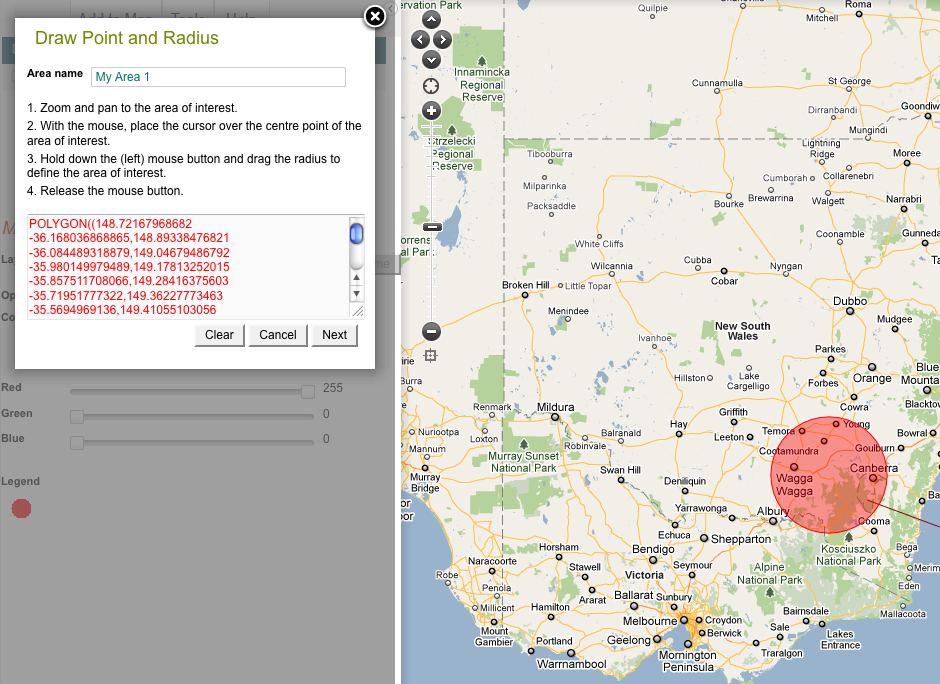
NOTE: The radius of the circle will be (dynamically) displayed on the top of the map window as you drag out the radius.
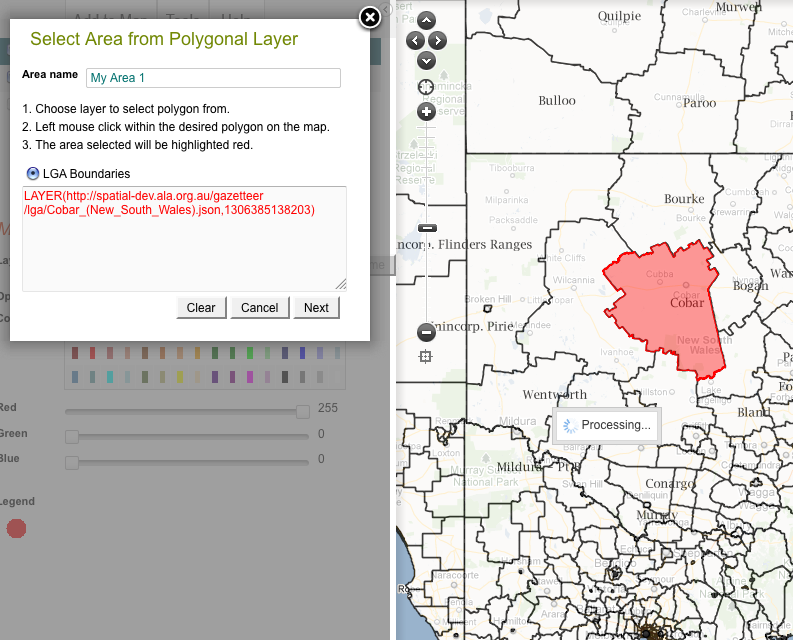
4. Select an Area from Mapped Polygonal Layer
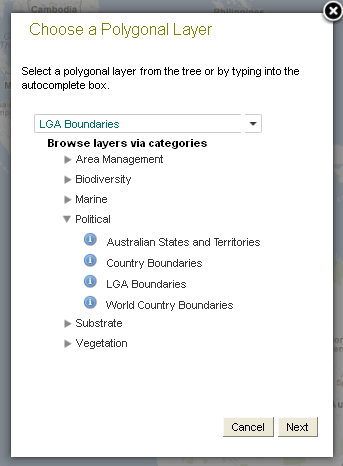
Select an area from a polygonal layer either by typing in the autocomplete text field, or by navigating the hierarchical tree of polygonal (contextual) categories.
Searching
Searching – searching allows the user to create a point and radius based on a Google geocode (address) lookup or search for a pre-defined polygon using the ALA gazetteer service.
5. Radius Centered on Street Address or Known Facility
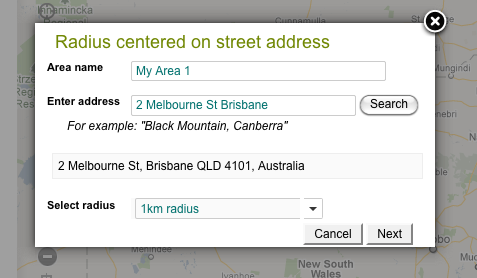
Enter an address and press “Search”, a successful geocode lookup will allow you to define a radius in kilometres (default is 1km). Press “Next” to add the location to the map. You can change the name of the “My Area” in the first text field. Features such as Queensland Museum and Sydney Opera House are also supported.
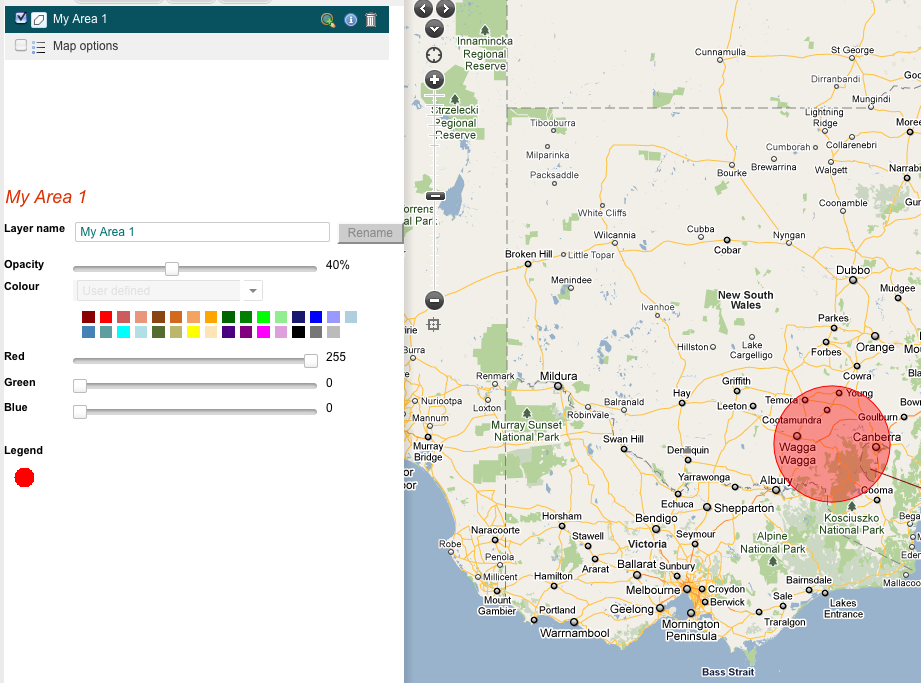
Use the zoom to extent button (magnifying glass) in the layer options to zoom in to the new area as pictured below.

6.Create radius from point (latitude, longitude)
This option requires that you enter
- The name of the area (this is what the layer produced will be called)
- A longitude in decimal degrees
- A latitude in decimal degrees
- A radius in kilometers

A circular area with the specified radius is then generated at the specified location.

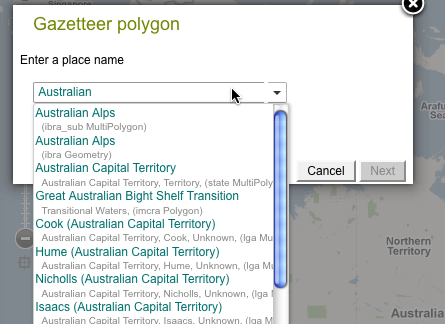
7. Gazetteer polygon
The ALA Gazetteer has over a 600,000 named points that can be added to the map. For a complete list of Spatial Portal contextual gazetteer layers that support gazetteer (named areas), see to http://spatial.ala.org.au/webportal/.
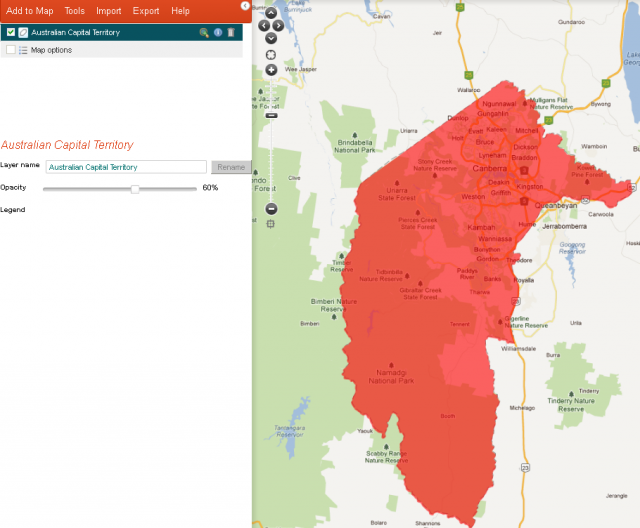
Preset Areas
Preset Areas – allows the user to select the entire world, just Australia or the current map view.
8. Box – Australia
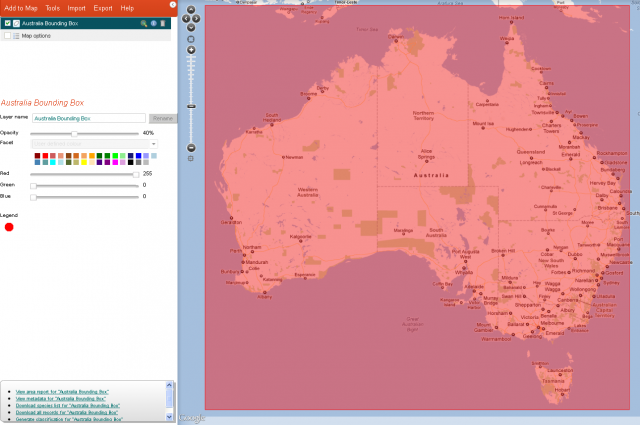
The Australian bounding box only covers mainland Australia, including Tasmania. It does not include Australian territorial islands and the Australian subantarctic islands or the Australian Exclusive Economic Zone. The bounding box captures Australia waters off Papua New Guinea and intersects with the lower bottom edge of Papua New Guinea, Timor-Leste and a couple of southern Indonesian islands.
9. Box – World
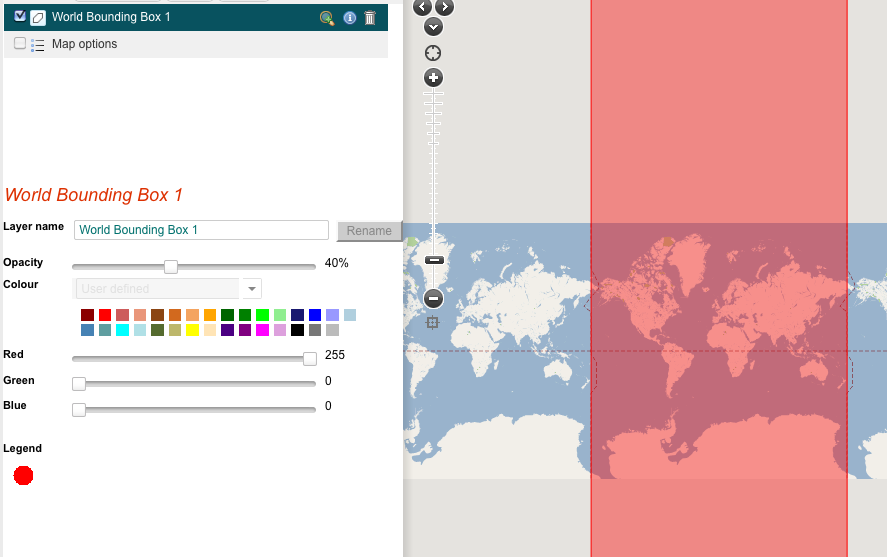
However, the standard projection used by the Spatial Portal does not permit the use of a bounding box > ~85 degrees north and south of the equator. More info »
10. Box – Current View (extent)
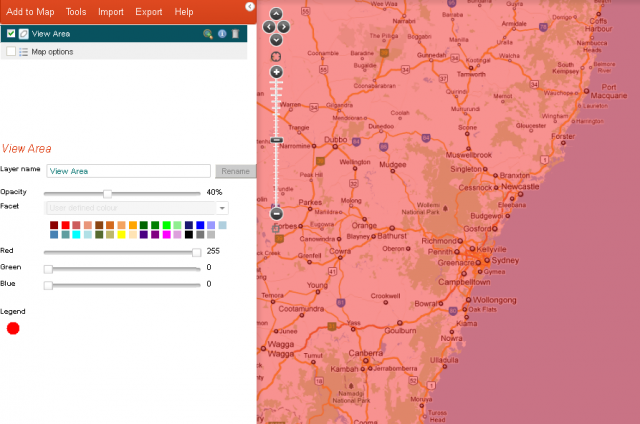
Whatever is visible in the map, whether you are zoomed in or out, is the current view of the map. Also known as the current extent. Selecting Box – Current View draws a bounding box around this extent.
Upload
Upload – allows the user to upload either a zip file containing an ESRI shape file or Google Earth KML polygon definition.
11. Upload Shapefile
Click for more information on uploading a Shape File »
12. Upload KML
Click for more information on uploading a KML »
Other
Other – provides three additional mechanisms to define an area. Defining an environmental envelope, the ability to paste in a well known text (WKT) polygon definition and the ability to be able to MERGE a set of currently defined areas.
13. Define environmental envelope
An environmental envelope allows you to specify one or more environmental conditions to define an area on the map. The definition of each added environmental layer condition is ANDed: The addition of each condition will reduce the geographic area corresponding to the environmental envelope. The limit to the number of layers added is the total number of environmental layers available in the Spatial Portal.
The key purpose behind this option is to help facilitate the identification of geographic areas where optimal ‘living conditions’ exist for flora and fauna. For example, ‘optimal’ locations for growing a particular grape variety may be identified, if the known parameters exist with layers help by the Spatial Portal.
A single Environmental layer has been added to the Map to show Annual Mean Temperature between 22 and 26 degrees.
Note that only one set of contiguous values can be defined for each added layer. For example, a mean annual temperature between 15 and 20c is acceptable but <10c and >15c is not. Re-adding a layer with different lower and upper limits will only ‘cookie cut’ the original envelope/area and not add to it.
14. Paste Well Known Text (WKT)
Click for more information on uploading a WKT »
15. Merge map areas
This is a new option that permits a set of predefined areas (each defined by a layer on the top-left of the Spatial Portal window) to be merged into one new layer that contains all the areas. This allows for great flexibility in defining areas. For example, an ‘area’ could be made of up a number of discrete IBRA regions or digitized polygons or imported with areas defined in the Spatial Portal.
The example below was generated by first digitzing three separate areas (rectangle, polygons and circle) and then using this option to combine the three separate areas into one new definition of area.
